TYLENOL® Efficacy
Proven, effective pain relief in a wide range of conditions and patients
The analgesic efficacy of TYLENOL® has been well supported by clinical studies
As effective as the maximum OTC dose and Rx dose of ibuprofen in osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee1*
Delivers comparable pain relief to ibuprofen for sprains and strains2
Effectively manages post-op dental pain at 1000 mg and 650 mg3
Analgesic Efficacy in OA
At 4 weeks, acetaminophen was shown to be as effective as ibuprofen for short-term, symptomatic treatment of OA pain of the knee1
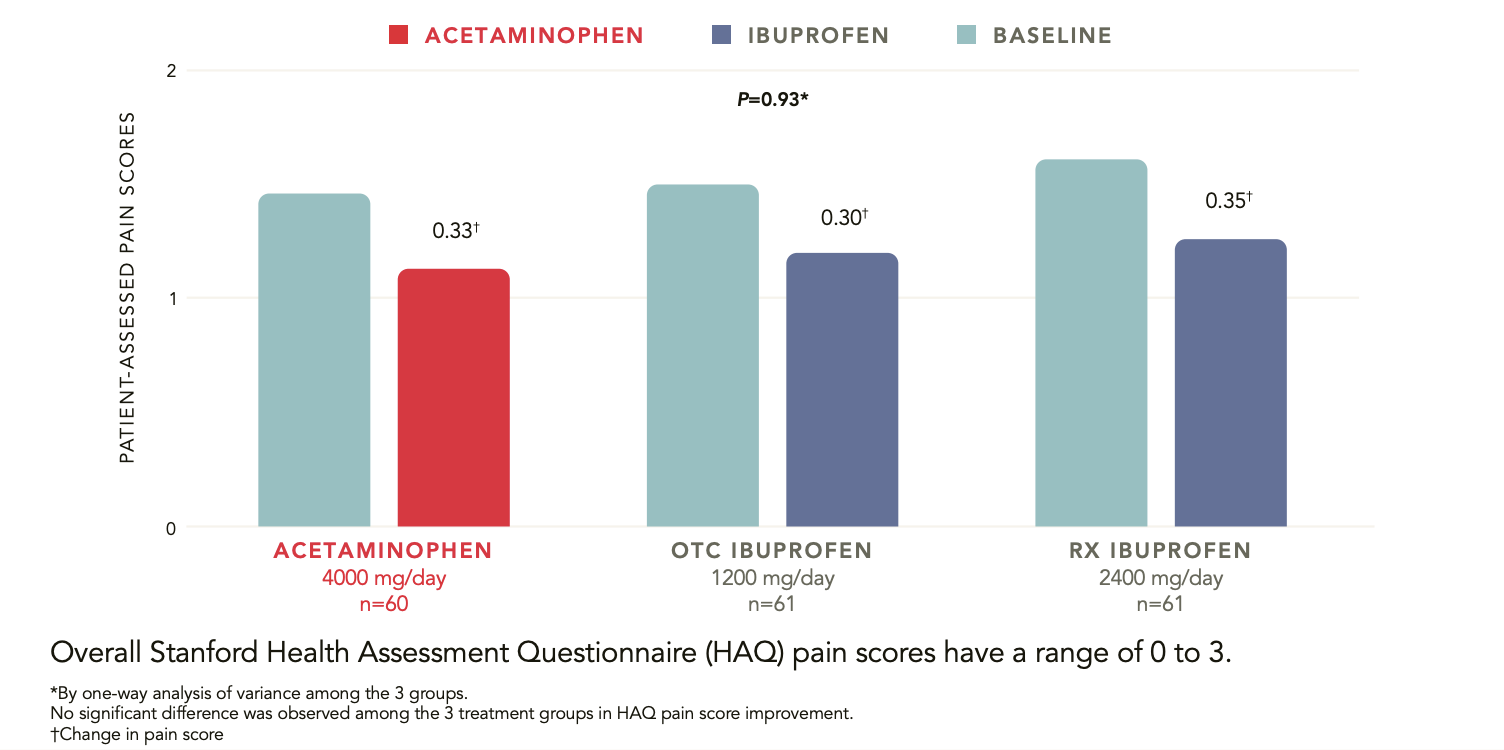
Overall Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) pain scores have a range of 0 to 3. By one-way analysis of variance among the 3 groups. No significant differences were observed among the 3 treatment groups.
Study Design
Randomized, double-blind
184 patients with chronic grade 2 (mild) or grade 3 (moderate) OA knee pain
Mean age: 55 to 57; 71%-79% female
Groups: acetaminophen 4000 mg/day, ibuprofen 1200 mg/day, or ibuprofen 2400mg/day
4 weeks
Outcome measures: HAQ pain scores, et al
Analgesic Efficacy in Sprains and Strains
Acetaminophen extended-release 3900 mg/day: comparable to ibuprofen 1200 mg/day for grade I or II lateral ankle sprains2
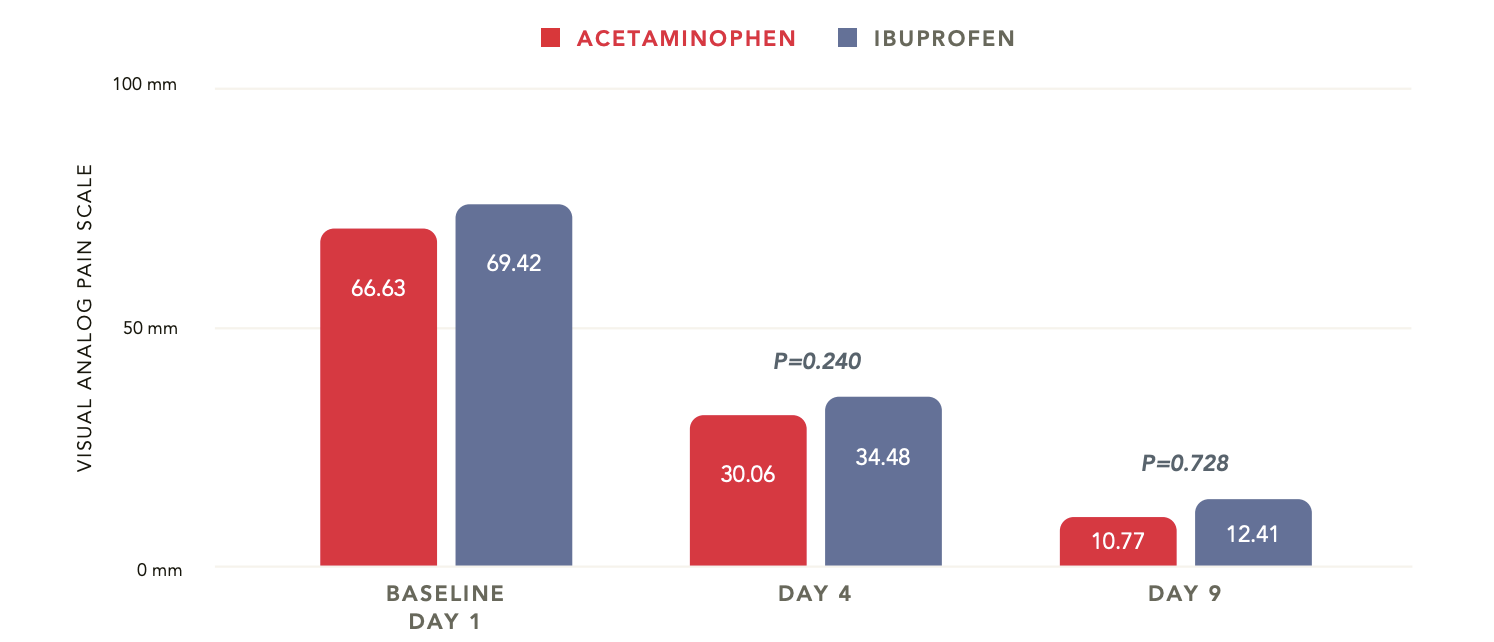
Study Design
Randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial
260 patients with grade I or II lateral ankle sprains
Ages: ≥18 years
Groups: acetaminophen 3900 mg/day or ibuprofen 1200 mg/day
9 days
Primary endpoint: change from baseline at Day 4 in pain on walking
Analgesic Efficacy at 1000 mg & 650 mg
Acetaminophen 1000 mg & 650 mg are effective in postoperative dental pain3
Sum of pain relief and pain intensity difference after dental extraction from baseline at each time point
P<0.001 for TYLENOL® 1000 mg vs placebo P<0.001 for TYLENOL® 650 mg vs placebo
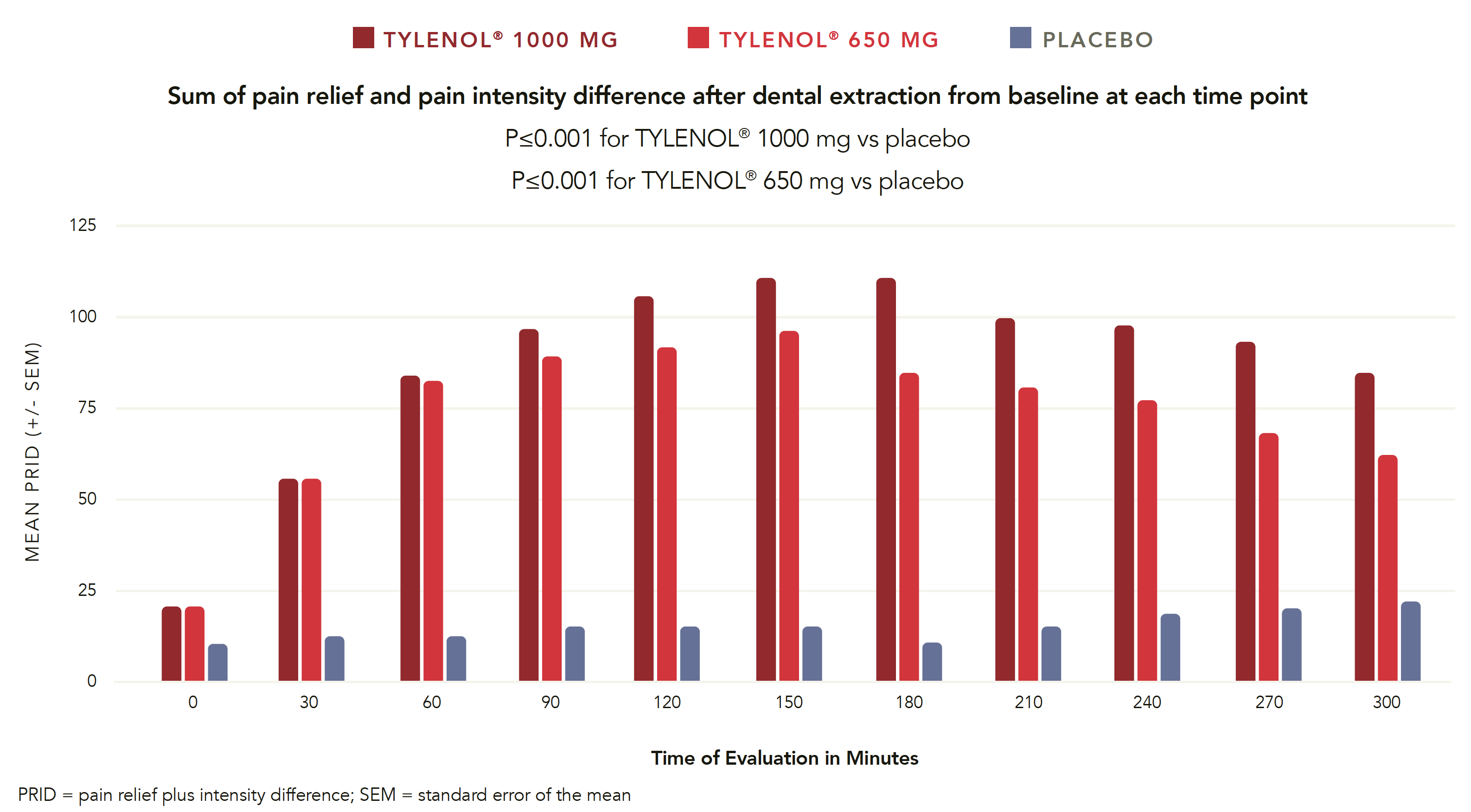
OTC=over-the-counter; PRID=pain relief plus intensity difference; SEM=standard error of the mean
Study Design
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose study
540 patients after surgical removal of impacted third molars
Pain level: at least moderate; score ≥50 on Visual Analog Scale (VAS) (0 to 100 mm)
Groups: acetaminophen 1000 mg, acetaminophen 650 mg, or placebo
Ages: 16 to 50 years
1 dose
Measures: pain intensity and pain relief over 6 hours (VAS) Adapted from: Qi DS et al. Clin Ther. 2012;34(12):2247-2258.
*Using maximum dose of acetaminophen.
References
1. Bradley JD, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Kalasinski LA, Ryan SI. Comparisonof an antiinflammatory dose of ibuprofen, an analgesic dose of ibuprofen, and acetaminophen in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med.1991;325(2):87-91.
2. Dalton JD Jr, Schweinle JE. Randomized controlled noninferiority trial to compare extended release acetaminophen and ibuprofen for the treatment of ankle sprains. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;48(5):615-623.
3. Qi DS, May LG,Zimmerman B, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study ofacetaminophen 1000 mg versus acetaminophen 650 mg for the treatment of post surgical dental pain. Clin Ther. 2012;34(12):2247-2258.